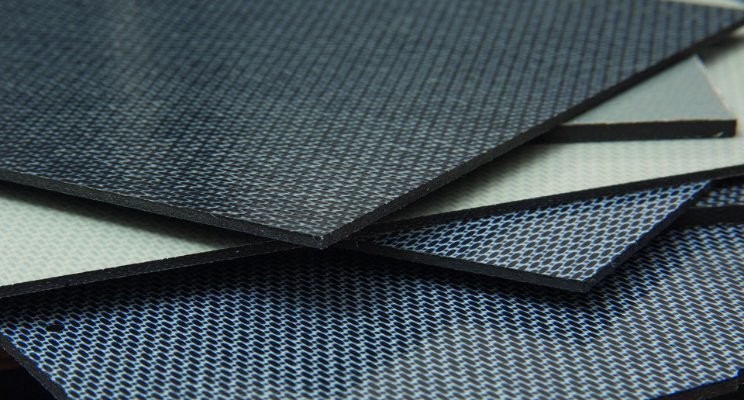
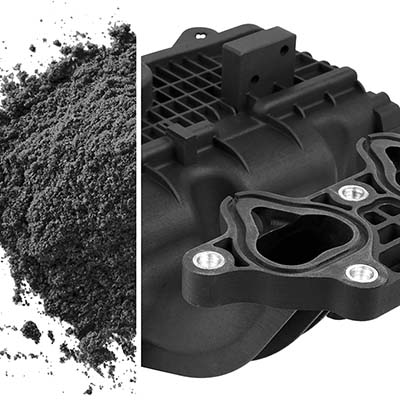
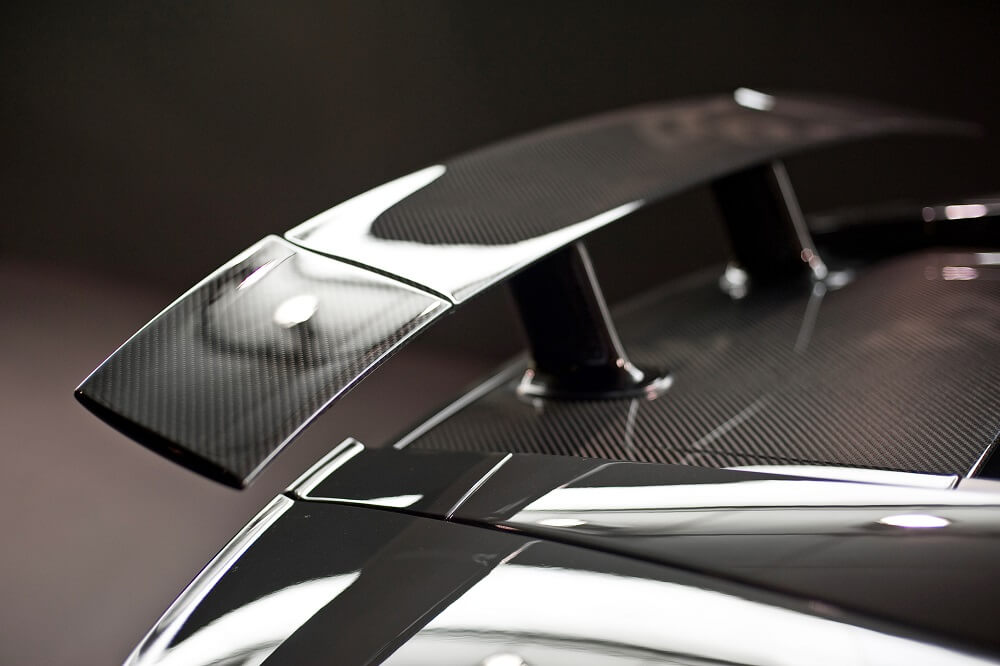
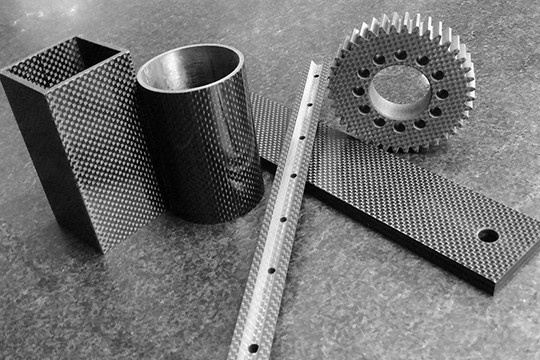
With the continuous development of composite materials, in addition to glass fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, boron fiber-reinforced plastics, etc. have appeared. Carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites (CFRP) are lightweight and strong materials that are used to manufacture many products that we use in our daily lives. It is a term used to describe fiber-reinforced composite materials that use carbon fibers as the main structural component.
Table of Content:
1. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Structure
2. The Molding Method of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic
3. Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer
4. Advantages of CFRP
5. Disadvantages of CFRP
6. Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastic Uses
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Structure
Carbon fiber reinforced plastic is a material formed by arranging carbon fiber materials in a certain direction and using bonded polymer materials. The diameter of carbon fiber is extremely thin, about 7 microns, but its strength is extremely high.
The most basic constituent unit of carbon fiber reinforced composite material is carbon fiber filament. The basic raw material of carbon filament is prepolymer polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or petroleum pitch. The carbon filaments are then made into carbon fiber fabrics by chemical and mechanical methods for carbon fiber parts.
The binding polymer is usually a thermosetting resin such as epoxy. Other thermosets or thermoplastic polymers are sometimes used, such as polyvinyl acetate or nylon. In addition to carbon fibers, composites can also contain aramid Q, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, aluminum, or glass fibers. The properties of the final carbon fiber product can also be affected by the type of additives introduced into the bonding matrix.
The Molding Method of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic
Carbon fiber products are mainly different due to different processes. There are many methods for forming carbon fiber reinforced polymer materials.
1. Hand Lay-up Method
Divided into the dry method (pre-prepared shop) and wet method (fiber fabric and resin glued to use). Hand lay-up is also used to prepare prepregs for use in secondary molding processes such as compression molding. This method is where sheets of carbon fiber cloth are laminated on a mold to form the final product. The strength and stiffness properties of the resulting material are optimized by selecting the alignment and weave of the fabric fibers. The mold is then filled with epoxy and cured with heat or air. This manufacturing method is often used for non-stressed parts, such as engine covers.
2. Vacuum Forming Method
For the laminated prepreg, it is necessary to apply pressure through a certain process to make it close to the mold and to cure and shape it under a certain temperature and pressure. The vacuum bag method uses a vacuum pump to evacuate the inside of the forming bag so that the negative pressure between the bag and the mold forms a pressure so that the composite material is close to the mold.
On the basis of the vacuum bag method, the vacuum bag-autoclave forming method was derived later. Autoclaves provide higher pressures and heat cure the part (instead of natural curing) than vacuum bag-only methods. Such a part has a more compact structure, better surface quality, can effectively eliminate air bubbles (bubbles will greatly affect the strength of the part), and the overall quality is higher. In fact, the process of vacuum bagging is similar to that of mobile phone film sticking. Eliminating air bubbles is a major task.
3. Compression Molding Method
Compression molding is a molding method that is conducive to mass production and mass production. Molds are usually made of upper and lower parts, which we call male mold and a female mold. The molding process is to put the mat made of prepregs into the metal counter mold, and under the action of certain temperature and pressure, the mat is heated and plasticized in the mold cavity, flows under pressure, and fills the mold cavity, and then And molding and curing to obtain products. However, this method has a higher initial cost than the previous ones, since the mold requires very high-precision CNC machining.
4. Winding Molding
For parts with complex shapes or in the shape of a body of revolution, a filament winder can be used to make the part by winding the filament on a mandrel or core. After winding is complete cure and remove the mandrel. For example, tubular joint arms used in suspension systems can be made using this method.
5. Resin Transfer Molding
Resin transfer molding (RTM) is a relatively popular molding method. Its basic steps are:
1. Place the prepared bad carbon fiber fabric in the mold and close the mold.
2. Inject liquid thermosetting resin into it, impregnate the reinforcing material, and cure.
Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer
(1) High strength and good elasticity.
The specific strength (that is, the ratio of tensile strength to density) of carbon fiber is 6 times that of steel and 17 times that of aluminum. The specific modulus (that is, the ratio of Young’s modulus to density, which is a sign of the elasticity of an object) is more than 3 times that of steel or aluminum.
With high specific strength, it can bear a large working load. Its maximum working pressure can reach 350 kg/cm2. In addition, it is more compressible and resilient than pure F-4 and its braid.
(2) Good fatigue resistance and wear resistance.
Its fatigue resistance is much higher than that of epoxy resin and higher than that of metal materials. Graphite fibers are self-lubricating and have a small coefficient of friction. The amount of wear is 5-10 times smaller than that of general asbestos products or F-4 braids.
(3) Good thermal conductivity and heat resistance.
Carbon fiber reinforced plastics have good thermal conductivity, and the heat generated by friction is easily dissipated. The interior is not easy to overheat and store heat and can be used as a dynamic sealing material. In the air, it can work stably in the temperature range of -120~350°C. With the reduction of alkali metal content in carbon fiber, the service temperature may be further increased. In an inert gas, its adaptable temperature can reach about 2000°C, and it can withstand sharp changes in cold and heat.
(4) Good vibration resistance.
It is not easy to resonate or flutter, and it is also an excellent material for vibration reduction and noise reduction.
Advantages of CFRP
1. Light Weight
Traditional glass fiber reinforced plastics use continuous glass fibers and 70% glass fibers (glass weight/total weight) and typically have a density of 0.065 pounds per cubic inch. A CFRP composite with the same 70% fiber weight typically has a density of 0.055 pounds per cubic inch.
2. High Strength
Although carbon fiber reinforced polymers are lightweight, CFRP composites have higher strength and higher stiffness per unit weight than glass fiber composites. Compared with metal materials, this advantage is more obvious.
Disadvantages of CFRP
1. High Cost
The production cost of carbon fiber reinforced plastic is prohibitive. Carbon fiber prices can vary dramatically depending on current market conditions (supply and demand), the type of carbon fiber (aerospace vs. commercial grade), and the size of the fiber bundle. On a pound-for-pound basis, virgin carbon fiber can be 5 to 25 times more expensive than glass fiber. This difference is even greater when comparing steel to CFRP.
2. Conductivity
This is the advantage and disadvantage of carbon fiber composite materials. It depends on the application. Carbon fibers are extremely conductive and glass fibers are insulating. Many products use fiberglass instead of carbon fiber or metal because they require stringent insulation. In the production of utilities, many products require the use of glass fibers.
Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastic Uses
The applications of carbon fiber reinforced polymer are wide in life, from mechanical parts to military materials.
(1) as sealing packing
Carbon fiber reinforced PTFE material can be made into corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and high-temperature-resistant sealing rings or packing. When used for static sealing, the service life is longer, more than 10 times longer than that of general oil-immersed asbestos packing. It can maintain sealing performance under load changes and rapid cooling and rapid heating. And since the material does not contain corrosive substances, no pitting corrosion will occur on the metal.
(2) as grinding parts
Utilizing its self-lubricating properties, it can be used as bearings, gears, and piston rings for special purposes. Such as oil-free lubricated bearings for aviation instruments and tape recorders, oil-free lubricated gears for electric transmission diesel locomotives (to avoid accidents caused by oil leakage), oil-free lubricated piston rings on compressors, etc. In addition, it can also be used as sliding bearings or seals in the food and pharmaceutical industries by taking advantage of its non-toxic characteristics.
(3) As structural materials for aerospace, aviation, and missiles. It was first used in aircraft manufacturing to reduce the weight of the aircraft and improve flight efficiency. It is also used in chemical, petroleum, electric power, machinery, and other industries as a rotary or reciprocating dynamic seal or various static seal materials.
Zhengxi is a professional hydraulic press factory in China, providing high-quliaty composite hydraulic press for forming CFRP products.
Post time: May-25-2023